Now that you understand the position concept we are going to expand on that by looking at the subject of which starting hands to play and which to throw in the muck.
- All Texas Hold’em starting hands can be separated into two categories: “suited” and “offsuit”. Suited hands contain two cards of the same suit, like J♣9♣, A ♥ K ♥, K♠Q♠ and 9 ♦ 3 ♦. All other starting hands are in the offsuit category, like A♠8 ♦, 7♣5 ♥ and K ♥ 9 ♦.
- The starting hand ranking or strength is always sorted by the 6-man game winning probability. Unfortunately, this will cause the 9-man winning chance to be not sorted perfectly. There are 2 possible reason: (i) We need to do more simulations to improve the accuracy of the estimated odds, or (ii) Game dynamics in a 9 players game are indeed slightly different.
- An ace-high straight flush, commonly known as a royal flush, is the best possible hand in many variants of poker. In poker, players form sets of five playing cards, called hands, according to the rules of the game. Each hand has a rank, which is compared against the ranks of other hands participating in the showdown to decide who wins the pot.
Poker Hand Rankings - Texas Holdem Starting Hands Chart. At the bottom of this page is a comprehensive listing of Texas Hold'em starting hands based on their EV (expected value). Expected value is the average number of big blinds this hand will make or lose. For example: AA from the Small Blind in a $3/$6 game will make, on average, 2.71. Against AK, AQ, AA, KK, QQ, you are a big underdog. Other typical raising hands like JJ, TT, 99, AJs, are slightly ahead of you as well. The only time you might call or re-raise is from late position, if the opener was in middle or late position, indicating they might have a wider range of hands.
This is the area where inexperienced players become fish, simply by not having the ability to fold weak hands before the flop. You can save a lot of money at this stage of the hand just by simply choosing not to play.
The Importance of Starting Hand Selection
As you know Poker is a game of maths and probability. It is therefore possible to know which starting hands are most probable to win a hand and this has been statistically proven in many studies. These studies have been able to rank starting hands according to how likely they are to win the hand against a random selection of opponent’s starting hands.
Starting hand
By Starting Hand we mean the two hole cards which are dealt to you at the start of each hand.
Since we now know which are the best starting hands in poker then we can apply this knowledge to our strategy. Remember, when we play a hand, we want to play with the odds in our favour, and by selectively choosing which starting hands we play we can ensure this.
Of course if we just waited for the two or three best poker starting hands then we wouldn’t actually play many hands as the probability of these cards being dealt is only once in a while.
So we combine the position concept with our starting hand concept, to allow us to only play a narrow starting hand selection when out of position and to play a wider range of starting hands when we are in position. Therefore the benefit of playing in position makes up for the weaker starting hands we may play.
Starting Hand Groups
You could look at all the statistical information and studies, but we’ve taken all the work out of it for you. The following section is a key part of your strategy and you should practise choosing the right action before the flop using the poker starting hands chart below.
We have chosen 46 different hands that we will play depending on the position and situation we are in. Those 46 hands have been separated into 8 groups named Group A to H. Group A are the strongest hands in poker based on the statistics and group H are the weakest hands that we are willing to play. Of course there are many more hand combinations weaker than the hands in Group H, but we are not interested in playing with these and they will be folded into the muck straight away.
Group B
AK
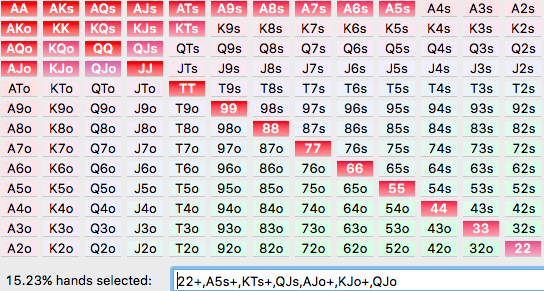
Group D
AQs
AQ
AJs
99
88
Group F
AT
KQ
KJs
QJs
44
33
22
Group H
KJ
KT
QJ
J8s
T8s
87s
76s
The ‘s’ next to some of the hands stands for Suited, so two cards of the same suit. ‘AJs’ could stand for A J whereas ‘AJ’ could stand for A J
Take a minute just to browse the hands in each group, you don’t need to memorise these, as you can use the chart to refer to, and once you have used it for a while, you will start to remember which hands are in which groups.
Poker Starting Hand Charts
Ok, so now we have our selection of 46 hands, and have split them into 8 groups based on strength, now what? Well we won’t just automatically play any of those 46 hands when they are dealt to us, we will make a decision based on the position we are in, and the situation we are faced with at the table.
When we are in position we will play a wider range of groups and out of position we will only play the stronger groups. Similarly when opponents have shown strength at the table by raising we will only play the better cards against them.
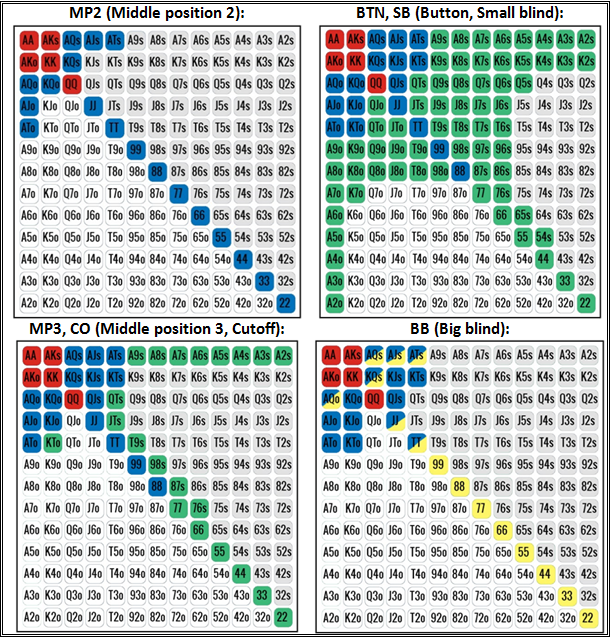
There are three charts, UNRAISED, RAISED and BLINDS. These are our Action charts, and show us what action to take when we have a hand in one of the starting hand groups.
The three charts are:
- UNRAISED – When everybody acting before you has either folded or called the big blind.
- RAISED – When somebody acting before you has raised.
- BLINDS – When you are in either the small blind or the big blind position and somebody acting before you has raised
| UNRAISED | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Everybody acting before you has either Folded or Called the Big Blind | ||||
| Action | Early Position | Mid Position | Late Position | |
| Opening Raise | A B C D | A B C D E | A B C D E F | |
| Call a Re-Raise | B C | C | C D | |
| Raise a Re-Raise | A | A B | A B | |
| Call the Big Blind (if Multiway Pot) | F G | G H | ||
| RAISED | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Someone acting before you has Raised already | ||||
| Action | Early Position | Mid Position | Late Position | |
| Re-Raise | A B | A B | A B | |
| Call | C | C | C D | |
| BLINDS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After a Raise and You are in the Blinds | ||||
| Action | Raised from Early Position | Raise from Mid Position | Raised from Late Position | |
| Unraised Blinds – Play as if you were in Late Position in the Unraised chart | ||||
| Re-Raise | A | A B C | A B C D | |
| Call | B C D | D E | E F | |
To use the charts, just follow these steps:
- What group is your starting hand in? if it isn’t in any group then you Fold.
- What Situation are you in? Choose one of the three action charts relevant to the situation you are in.
- What Position are you in? Look at the column in the chart for the position you are in.
- Starting Hand Group not shown? If your starting hand group is not shown in that column, then you Fold.
- Starting Hand Group Shown? If your starting hand group letter is shown then take the action the chart is showing you.
The different actions in each of the charts are:
- Opening Raise – Make the first Raise
- Call – Just Call when a person has Raised
- Re-Raise – Re-Raise a person who has Raised
- Call a Re-Raise – Call when someone Re-Raises your original Raise
- Raise a Re-Raise – Re-Raise when somebody has Re-Raised your original Raise
- Call the Big Blind – Just call the big blind amount (also known as ‘limping in’)
Quick Reference
I don’t expect you to memorise all the starting hand groups and action charts. The way to learn them is by putting them into practise and then over time you will start to memorise them. But to start with, you can refer to the charts while you are playing.
You can either just bookmark and pull this page up each time you play or we have a couple of other methods to make your life a bit easier.
Printable Starting Hands Chart
A neat and tidy, A4 size starting hand chart which you can print and keep in front of you for quick reference while you are playing.
To download the Starting Hands Chart right click on the link and select save target as.
It is a PDF file, so to view and print this you will need the free Adobe Acrobat Reader. If you don’t have this you can download it here.
Starting Hands Chart Desktop Wallpaper
Use this as your computer desktop wallpaper. It is designed so that whilst you are playing poker, you can place your poker table window over the Poker Professor logo and all the charts will be visible around the table. Neat huh!
To download the Starting Hands Wallpaper right click on the link and select save target as.
To set as your desktop wallpaper, right click on the file you have just downloaded and select “Set As Desktop Background”.
The wallpaper is optimised for a desktop screen size of 1920×1080 as this is the most common. It should work with most other desktop sizes as well as windows should automatically resize it for you.
Starting Hand Examples
Lets take a look at some example starting hands and walk through what the charts are telling you to do and what thought process to follow.
Example Hand 1
You are sitting in early position and are dealt A J. You are first to act and so nobody has bet before you.
- What group is my hand in – AJ is a Group E hand
- What situation am I in – Nobody has raised before me so UNRAISED
- What position am I in – Early Position
So from the answers to the above questions we look at the UNRAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Early Position. You will see that Group E is not shown in that column so we are not allowed to play a Group E hand in Early position in this situation and so we would fold this hand.
Example Hand 2
You are sitting in early position and are dealt A K. You are first to act and so nobody has bet before you.
- What group is my hand in – AK is a Group B hand
- What situation am I in – I am first to act so it is UNRAISED
- What position am I in – Early Position
So from the above we look at the UNRAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Early Position. You will see that with a group B hand we are told to make an opening raise. So we would enter the hand by making a Raise (We will look at details of how much to raise later in the lesson).
Example Hand 3
You are sitting in Mid Position and are dealt A A. A Player in early position has raised the pot up to 3 times the Big Blind.
- What group is my hand in – AA is the best starting hand and therefore a Group A hand
- What situation am I in – There has been a raise by a player in early position, so it has been RAISED
- What position am I in – Mid Position
Poker Best Starting Hands
So, we look at the RAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Mid Position. You will see that with a group A hand we are told to make a Re-Raise. So we would enter the hand by making a Re-Raise. (We will look at details of how much to raise later in the lesson)
Example Hand 4
You are sitting in Mid Position and are dealt 9 9. A Player in early position has raised the pot up to 3 times the Big Blind.
- What group is my hand in – 99 is a Group D hand
- What situation am I in – There has been a raise by a player in early position, so it has been RAISED
- What position am I in – Mid Position
So, again we look at the RAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Mid Position. You will see that we are not allowed to play an already RAISED pot in Mid Position with a group D hand. So we fold this hand.
Example Hand 5
You are sitting in Late Position and are dealt 8 7. Two Players acting before you have limped in and called the big blind.
- What group is my hand in – 87s is a Group H hand
- What situation am I in – There has been two limpers, but no raise, so it is UNRAISED
- What position am I in – Late Position
So, we look at the UNRAISED Action chart, and look in the column for Late Position. You will see that we are allowed to Call a Multi-way pot with a group H hand (multiple players playing the hand). As two people have already called and the blinds will likely also call we can call the big blind and play the hand. So we would call the big blind on this hand.
How much should I Raise?
An opening Raise in general should be between 3 to 4 times the Big Blind. Anywhere in this range is ok, and as guide to start with I would raise the following amounts:
- When you are in EARLY POSITION Raise 4 times the Big Blind
- When you are in MID POSITION Raise 3.5 times the Big Blind
- When you are in LATE POSITION Raise 3 times the Big Blind
You should mix and match the size of your raises to prevent your opponents getting a read on your betting patterns, but the above can act as a general guide whilst you get used to your new strategy.
The reason to Raise more in Early position is because we are out of position and want to put as much pressure on our opponents as we can.
How much should I Re-Raise?
A Re-Raise should in general be between 2 – 4 times the original Raise, As a guide:
- When it has been Raised from EARLY POSITION Raise 2 times the Raise
- When it has been Raised from MID POSITION Raise 3 times the Raise
- When it has been Raised from LATE POSITION Raise 4 times the Raise
The reason for this is it is more likely that a player in late position has raised with a weaker hand than a player in Early position.
Practise Time
Well, that was a lengthy lesson and a lot to take in. Don’t worry, with practise it will start to become second nature, and that is exactly what you should do now with the first stage of your bankroll challenge.
Poker Starting Hands Excel
Poker Bankroll Challenge: Stage 1
- Stakes: $0.02/$0.04
- Buy In: $3 (75 x BB)
- Starting Bankroll: $25
- Target: $3 (1 x Buy In)
- Finishing Bankroll: $28
- Estimated Sessions: 1
Use this exercise to get used to selecting which starting hands to play and which not to play according to the Starting Hands chart and get used to understanding what position you are in at the table. Don’t get too carried away at this stage though, play conservatively and be aware that someone may have a better hand than you. We are going to learn in more detail about betting after the flop later in the course.
Omaha Hi-Lo is a fascinating game packed with action! The action, at least in small-middle stakes games, is not only loose but many times also weak. By having four cards, and playing for high and low, some players frequently find a “reason” to stick with their hand. However, even if their hand has some potential, pot odds often do not justify playing it. So, many novice players play too loosely, stick with their hands when they shouldn’t, and end up making many mistakes.
Most errors originate from poor preflop hand selection. Understanding which Omaha high-low starting hands are solid and under which circumstances they are playable will significantly improve your game!
Starting hands
The best starting hands in Omaha hi-lo have both strong high and low potential. Since aces are the best cards for high and low, they are excellent starting hands! Almost all playable starting hands contain at least an ace! On the counterpart, cards between six and nine, are considered weak. So, any starting hand containing one or more of these cards usually decreases in value.
Another deal-breaker is to have trips in your starting hand! This is because you can only use two out of three, so you have an unusable card in your hands. Your chances of hitting a set also decrease. Let’s take a look at the strongest starting hands.

Top hands
The best starting hand is AA23, followed by AA24. These hands have excellent high and low potential! If one, or even better, both aces are suited, the strength of the hand increases as it also has nut flush potential.
Powerful starting hands with both high and low potential
- AA, with one or two low cards (the smaller, the better), like AA2x or AA35
- A2 or A3 with two high cards, like AKJ2 or AKQ3
- A2 or A3, with a big pair, like KK or QQ
Strong only low starting hands
- A2 or A3 with one or two more low cards (the lower, the better), like A23x
- 2345, 2346, 2356 (the flop must contain an ace, and at least another small card, or the hand may become useless)
Note that if one or no low cards come on the flop, these hands lose their value
Strong only high starting hands
- AA, with two high cards, like AAKJ
- A with three cards ten or higher, like AKJ10 or AKQJ
- Four high connected cards, like KQJ10 or QJ109
- High cards with one pair, like KKQJ, or KQQJ
- Double paired high cards, like KKQQ
Note that if three or even two low cards appear on the flop, these hands go down in value. So you should adjust your play accordingly.
Trouble starting hands to avoid
Unlike Holdem, in Omaha hi-lo, it is ok to play a little looser preflop. The idea is to try to see many flops with hands that have potential. However, you must remain selective and avoid some trouble hands, especially when playing in a full table.
Some hands may seem attractive, but will only make second or third best! Don’t play them as they have a negative expected value. For example, avoid playing A4x or A5x type of hands in a full table, as they may get you in trouble more often than not.
The same goes for the high. With everyone having four cards, it is more probable that someone will make a monster hand, so you don’t want to be drawing for second or third best! For example, if you are drawing for a queen-high flush, you will often lose to an ace or king-high flush. Even if you make a set of nines, you will often end up second best to a higher set! Let’ take a look at some other trap hands.
Poker Starting Hands Winning Percentages
- 333A, AAA4 type hands have minimal high potential, and even if they make a low, it may be second-best.
- 9876, 8765, 7654 may seem keen but are really not! With these hands, it is tough to scoop the pot. If you make a nut straight, most of the time, there will be a low, and you will split the pot. If you make a straight with high cards, a better straight may beat you!
- High pairs with two one or two trash cards like KK9x or QQxx are weak hands. Do not confuse with the value of a pocket pair in Holdem. In Omaha hi-lo, with straight and flushes appearing often, a single pair is not all that great.
So, how to bet preflop?
Poker Starting Hands Chart
In Omaha hi-lo, taking the lead in the hand with preflop aggression is less crucial than in Holdem. So, raise preflop mostly for value when you have powerful hands and position.
From position, when several players have limped, you can widen your range and add in see cheap flops with some speculative hands. Raise with premium hands for value. Most of the limpers will call you, and you also want to build the pot to be able to make big bets after the flop.
Out of position, limp with hands that have both high and low potential, to see a multiway flop.
Multiplayer versus heads-up preflop requirements
Some of the hands that are not good enough for a multiway pot go up in value heads-up. When playing in a multiway pot, you want your hand to have nut, or close to nut potential for the high and low. When playing heads up, you can win the low or high with medium-strength hands. For example, heads-up A4 is often good enough for the low, whereas in a multiway pot, it is a weak hand.
Also, heads-up you can win the high with a hand like two pair or a set, even when the board has some flush or straight possibilities. If the board is dry, even top pair-top kicker can win you the pot! In a multiplayer pot, when the board has flush or straight potential, you should expect that someone will have it most of the time!
In a nutshell
In Omaha hi-lo, you often see players playing too loosely. By adopting a selective starting hand strategy, you gain a significant advantage over your opponents. In multiplayer pots, play hands that have strong high and low potential, and avoid hands that can give you second or third best!
I hope you found this post helpful. If you have any questions or suggestions that you want to share, please leave a comment below.